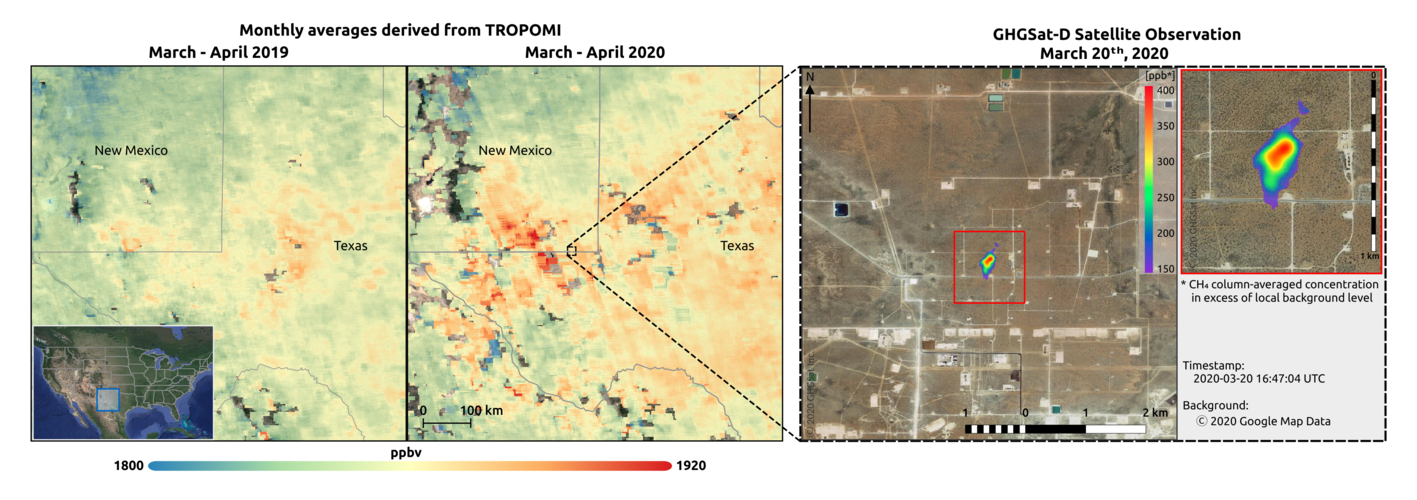
While carbon dioxide is more abundant in the atmosphere and therefore more commonly associated with global warming, methane is around 30 times more potent as a heat-trapping gas. Given its importance, Canadian company GHGSat have worked in collaboration with the Sentinel-5P team at SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research to investigate hotspots of methane emissions during COVID-19.
Click here for original story, Detecting methane emissions during COVID-19
Source: ESA Space News