In the vast tapestry of our universe lies a concept that stretches the boundaries of our understanding – the enigmatic Hubble volume. Named in homage to Edwin Hubble, the visionary astronomer who revolutionized our perception of the cosmos, this concept encapsulates the reachable expanse of our universe.
But what exactly is this cosmic entity, and why does it captivate the minds of astronomers and cosmologists alike? Join us as we delve into the Hubble volume, an ever-expanding domain of approximately 1031 cubic light-years.
What is the Hubble Volume?
The Hubble volume is a concept that helps us understand the vastness of our observable universe. It refers to the region of space that is within the reach of causality. This means that any object that is farther away from us than the Hubble volume is moving away from us faster than the speed of light. It is also known as Hubble sphere, Hubble bubble, subluminal sphere, causal sphere and sphere of causality.
The radius of the Hubble volume (known as the Hubble radius) can be calculated by dividing the speed of light by the Hubble constant. As we know from geometry, the radius to the power of three gives us the volume of a sphere. That’s how we get about 1031 cubic light-years as the current value of the Hubble volume. This is constantly growing as the universe expands.
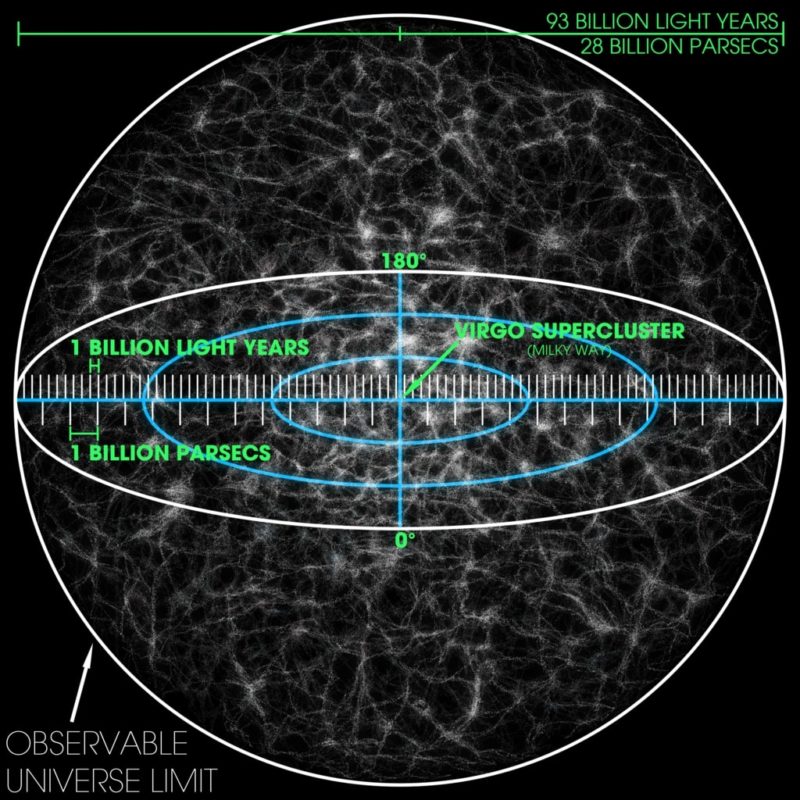
Hubble Volume vs Observable Universe
The Hubble volume is actually smaller than the observable universe. It is a common misconception to confuse the two. Because of the expansion of the universe, light from objects beyond the Hubble volume could reach us as the universe was much smaller in the past. The observable universe is simply everything we can theoretically observe from Earth, even if it’s currently moving away from us faster than the speed light due to the universe’s expansion.
What is the unit of Hubble?
The unit of Hubble is kilometers per second per megaparsec (km/s/Mpc). This unit is used to measure the rate at which the universe is expanding, known as the Hubble constant. The Hubble constant is a fundamental parameter in cosmology and represents the current expansion rate of the universe. It was first measured by astronomer Edwin Hubble in 1929, who discovered that galaxies were moving away from each other at a rate proportional to their distance.
The value of the Hubble constant has been refined over time through various observational methods, including observations of supernovae and measurements of cosmic microwave background radiation. Currently, there is some discrepancy between different measurements of the Hubble constant, leading to ongoing debates and research in cosmology.
Understanding the value of the Hubble constant is crucial for understanding the age and evolution of our universe. It helps astronomers calculate how far away distant objects are and how fast they are moving away from us. This information can then be used to infer important properties about our universe’s history, such as when it began and how it has evolved over time.
Conclusion
The Hubble volume, an expanding realm within our observable universe, defines the boundary of causality’s reach. It marks the limit where objects move away from us faster than light’s speed due to cosmic expansion.
In essence, the enigmatic Hubble volume, intertwined with the Hubble constant, unlocks fundamental insights into our universe’s dimensions, origins, and the mysterious tapestry of its evolution.