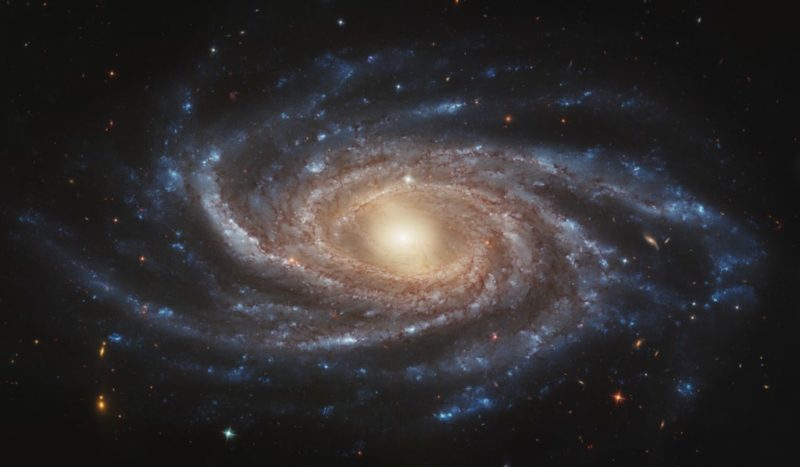

NGC 2336 is a remarkable barred spiral galaxy discovered by astronomer Wilhelm Tempel in 1876. What sets it apart from other galaxies is its unusual bar structure surrounded by a bright ring-like structure. Recent observations have shed light on the formation and evolution of this unique feature, making NGC 2336 a fascinating object of study for astronomers worldwide.
NGC 2336 Location
NGC 2336 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Camelopardalis, about 90 million light-years away from Earth. It is estimated to be about 200,000 light years across. With a few other galaxies it makes a galaxy group named the NGC 2336 group.

Exploring the Unique Features of NGC 2336
NGC 2336 is a unique barred spiral galaxy with several distinctive features that set it apart from other galaxies. One of the most notable features of this galaxy is its central bar, which is surrounded by a bright ring of stars. Additionally, it has at least 8 spiral arms that extend out from the central bar, giving it a distinctive shape.
The galaxy has a high level of star formation activity which is concentrated in the central bar and the spiral arms. As many as 28 H II regions, that may host young star clusters, have been observed in the galaxy
Another unique feature is its active galactic nucleus, which is thought to be powered by a supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy. This black hole is estimated to be at 30 million solar masses.
Finally, a type Ia supernova (SN 1987L) was discovered in this galaxy in 1987 by James Dana Patchick, an American amateur astronomer. It had an apparent magnitude of 14.2.
Conclusion
In its remote expanse, NGC 2336 stands as a cosmic marvel, captivating astronomers with its distinct bar structure, luminous ring, and a cosmic dance of spiral arms. Through recent observations, this barred spiral galaxy has unveiled its mysteries, offering a glimpse into the enigmatic mechanisms shaping its unique features. From the vibrant bursts of star formation to the dynamic presence of an active galactic nucleus powered by a colossal black hole, NGC 2336 continues to beckon scientists, remaining an intriguing celestial canvas for ongoing astronomical exploration and understanding.