After four years of delays, Europe’s new Ariane 6 rocket is set to blast off for the first time on Tuesday, carrying with it the continent’s hopes of regaining independent access to space.
The inaugural flight of the European Space Agency’s (ESA) most powerful rocket yet is scheduled to launch from Europe’s spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana at 3pm local time (1800 GMT).
Since the last flight of the rocket’s workhorse predecessor, Ariane 5, a year ago, Europe has been unable to launch satellites or other missions into space without relying on rivals such as Elon Musk’s US firm SpaceX.
So many will be nervously watching the launch, hoping it can bring an end to a difficult era for European space efforts.
Historically, nearly half of the first launches of new rockets have ended in failure.
That includes Ariane 5, which exploded moments after liftoff in 1996—but out of its 117 launches over nearly 20 years, only one other flight would fail.
Everyone at the Kourou launch site, which is surrounded by jungle on the South American coast, is hoping history does not repeat for Ariane 6.
“There is an element of risk because it is a first flight, but we have tried to reduce this as much as possible, so we are confident,” said Philippe Baptiste, head of France’s CNES space agency.
Tony dos Santos, the ESA’s Kourou technical manager, said that teams on the ground would only be able to “breathe our first sigh of relief when the first satellites have been released” an hour and six minutes after liftoff.

The launch plan
From dawn in Kourou, the vast metal structure housing the rocket will be moved away, unsheathing the 56-meter (183 feet) behemoth.
From 10am, its tanks will start to be filled with fuel.
From that point, any physical intervention would force the tanks to be emptied, requiring a 48-hour launch postponement, the ESA’s launch base project manager Michel Rizzi said.
Concealed in a nearby bunker, more than 200 experts in the launch center will scrutinize the rocket until liftoff, ready to interrupt the countdown to solve any problems, he added.
They will be in constant contact with the Jupiter control room, the hub of communication between the teams—and data sent from the rocket.
A large number of armed forces will also watch over the launch, including three fighter jets deployed to deter any curious aircraft nearby.

If there are issues ahead of liftoff, such as technical problems or inclement weather, there will be a four-hour launch window.
But all going well, the rocket’s two boosters and main stage engine will ignite at 3:00 pm local time.
Franck Saingou, Ariane 6 launch system architect, said there had been so many rehearsals that it all feels “routine—except this time it’s the real thing”.
Europe’s ‘return’ to space
The mission will be considered a success after it deploys its payload and the rocket’s reusable upper stage splashes down into the Pacific Ocean.
Ariane 6’s maiden flight will carry 17 different “passengers”, including 11 university micro-satellites, as well as re-entry capsules and small scientific experiments.
A successful flight would mark Europe’s “return” to the space scene, said ESA space transportation director Toni Tolker-Nielsen.
-
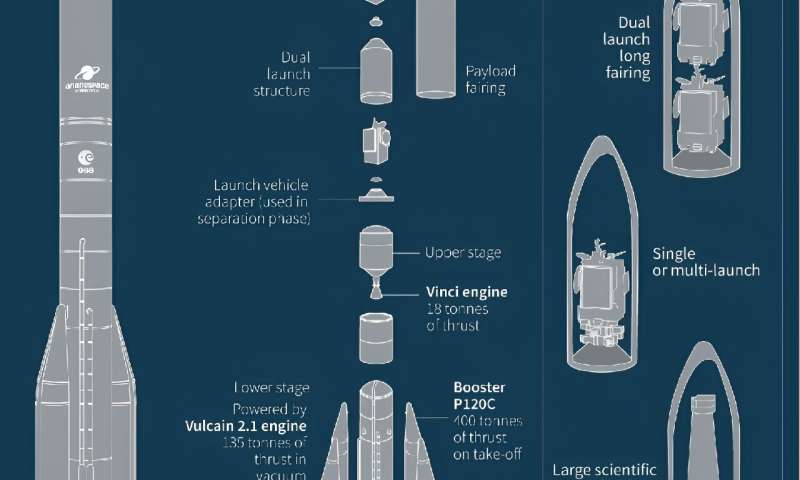
Europe’s Ariane 6 rocket.
-
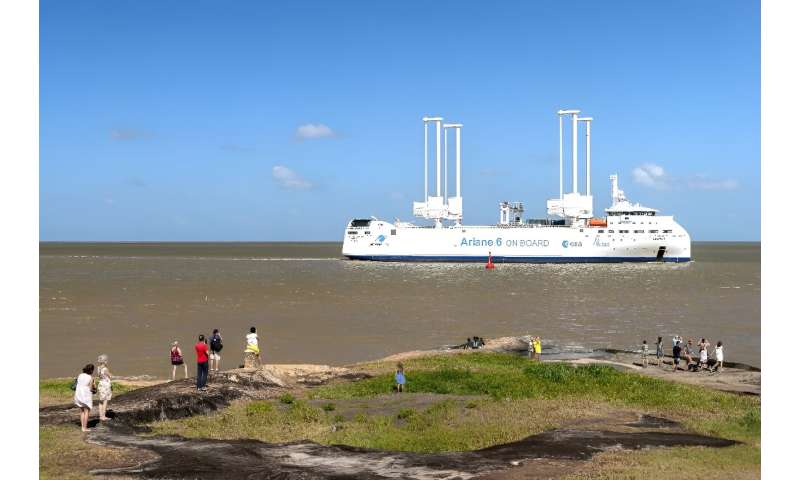

Ariane 6 crosses the Atlantic in a boat from Europe to French Guiana.
-
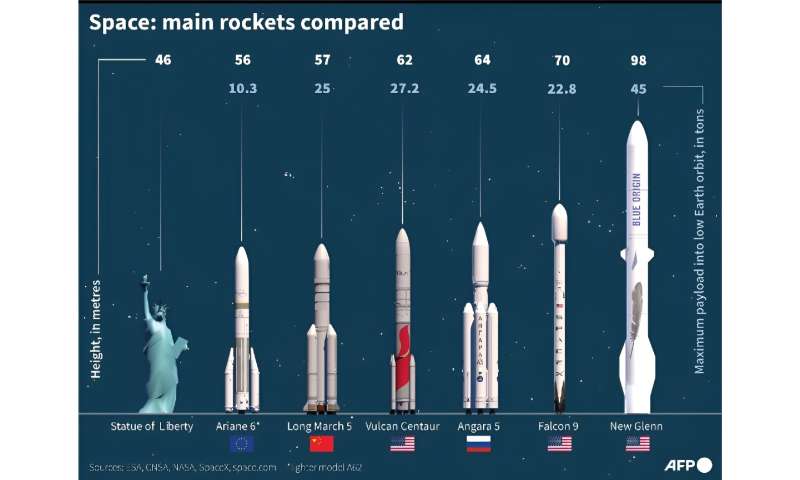
The main space rockets.
Russia pulled its Soyuz rockets, long used for European launches at Kourou, after Moscow invaded Ukraine in 2022.
Later that year, Europe’s Vega-C light launcher was grounded due to a launch failure. Delays to Ariane 6’s first flight—originally scheduled for 2020—further compounded the crisis.
Ariane 6 is scheduled for one more launch this year, six in 2025, then eight in 2026.
Gareth Dorrian, a space science researcher at the UK’s University of Birmingham, told AFP that “the first launch of any new rocket is always fraught”.
But Ariane 5 started with explosive failure and “went on to become one of the most successful launchers in history”, he added.
One of its last missions even took the $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope into space, he pointed out.
© 2024 AFP
Citation:
Countdown to first launch of Europe’s Ariane 6 rocket (2024, July 9)
retrieved 9 July 2024
from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.