A few years ago, astronomers uncovered one of the Milky Way’s greatest secrets: An enormous, wave-shaped chain of gaseous clouds in our sun’s backyard, giving birth to clusters of stars along the spiral arm of the galaxy we call home.
Naming this astonishing new structure the Radcliffe Wave, in honor of the Harvard Radcliffe Institute, where the undulation was originally discovered, the team now reports in Nature that the Radcliffe Wave not only looks like a wave, but also moves like one—oscillating through space-time much like “the wave” moving through a stadium full of fans.
Ralf Konietzka, the paper’s lead author and Ph.D. student at Harvard’s Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, explains, “By using the motion of baby stars born in the gaseous clouds along the Radcliffe Wave, we can trace the motion of their natal gas to show that the Radcliffe Wave is actually waving.”
Back in 2018, when University of Vienna professor João Alves was a fellow at Harvard Radcliffe Institute, he worked with Center for Astrophysics researcher Catherine Zucker—then a Ph.D. student at Harvard—and Alyssa Goodman, Robert Wheeler Willson Professor of Applied Astronomy, to map out the 3D positions of the stellar nurseries in the sun’s galactic neighborhood.
By combining brand-new data from the European Space Agency’s Gaia mission with the data-intensive “3D Dust Mapping” technique—pioneered by Harvard professor Doug Finkbeiner and his team—they noticed a pattern emerging, leading to the discovery of the Radcliffe Wave in 2020.
“It’s the largest coherent structure that we know of, and it’s really, really close to us,” said Zucker, who describes the collaboration’s work in a related Sky and Telescope article. “It’s been there the whole time. We just didn’t know about it, because we couldn’t build these high-resolution models of the distribution of gaseous clouds near the sun, in 3D.”
The 2020 3D dust map clearly showed that the Radcliffe Wave existed, but no measurements available then were good enough to see if the wave was moving. But in 2022, using a newer release of Gaia data, Alves’ group assigned 3D motions to the young star clusters in the Radcliffe Wave.
With the clusters’ positions and motions in hand, Konietzka, Goodman, Zucker and their collaborators were able to determine that the entire Radcliffe Wave is indeed waving, moving like what physicists call a “traveling wave.”
A traveling wave is the same phenomenon we see in a sports stadium when people stand up and sit down in sequence to “do the wave.” Likewise, the star clusters along the Radcliffe Wave move up and down, creating a pattern that travels through our galactic backyard.
Konietzka continued, “Similar to how fans in a stadium are being pulled back to their seats by the Earth’s gravity, the Radcliffe Wave oscillates due to the gravity of the Milky Way.”
Understanding the behavior of this 9,000 light year-long, gargantuan structure in our galactic backyard, just 500 light-years away from the sun at its closest point, allows researchers to now turn their attention to even more challenging questions. No one yet knows what caused the Radcliffe Wave or why it moves the way it does.
-
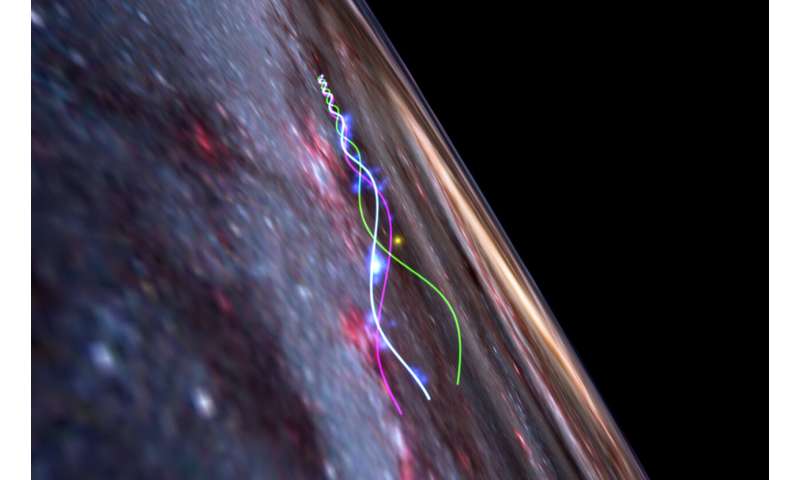

The Radcliffe Wave next to our sun (yellow dot), inside a cartoon model of the Milky Way. Blue dots are clusters of baby stars. The white line is a theoretical model by Ralf Konietzka and collaborators that explains the current shape and motion of the wave. The magenta and green lines show how the wave will move in the future. Credit: Ralf Konietzka, Alyssa Goodman, and WorldWide Telescope
-
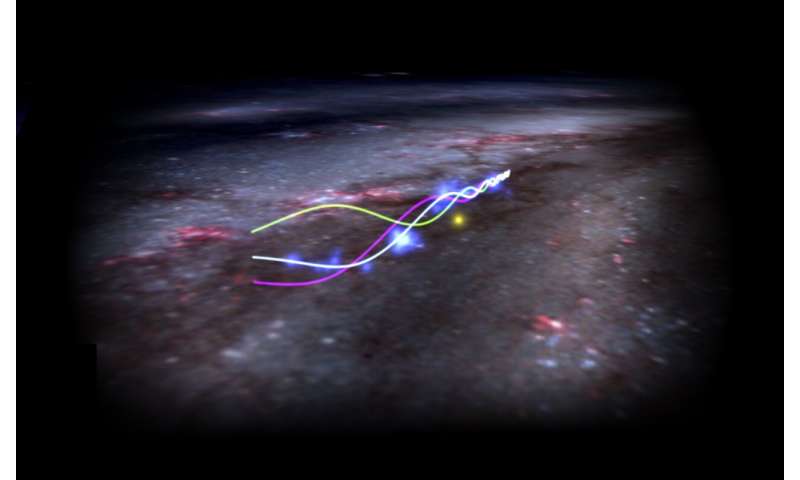
The Radcliffe Wave next to our sun (yellow dot), inside a cartoon model of the Milky Way. Blue dots are clusters of baby stars. The white line is a theoretical model by Ralf Konietzka and collaborators that explains the current shape and motion of the wave. The magenta and green lines show how the wave will move in the future. Credit: Ralf Konietzka, Alyssa Goodman, and WorldWide Telescope
“Now we can go and test all these different theories for why the wave formed in the first place,” Zucker said.
“Those theories range from explosions of massive stars, called supernovae, to out-of-galaxy disturbances, like a dwarf satellite galaxy colliding with our Milky Way,” Konietzka added.
The Nature article also includes a calculation of how much dark matter might be contributing to the gravity responsible for the wave’s motion.
“It turns out that no significant dark matter is needed to explain the motion we observe,” Konietzka said. “The gravity of ordinary matter alone is enough to drive the waving of the wave.”
In addition, the discovery of the oscillation raises new questions about the preponderance of these waves both across the Milky Way and other galaxies. Since the Radcliffe Wave appears to form the backbone of the nearest spiral arm in the Milky Way, the waving of the wave could imply that spiral arms of galaxies oscillate in general, making galaxies even more dynamic than previously thought.
“The question is, what caused the displacement giving rise to the waving we see?” Goodman said. “And does it happen all over the galaxy? In all galaxies? Does it happen occasionally? Does it happen all the time?”
More information:
The Radcliffe Wave is Oscillating, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07127-3. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07127-3
Provided by
Harvard University
Citation:
Astronomers observe the Radcliffe Wave oscillating (2024, February 20)
retrieved 20 February 2024
from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.